第04章_IDEA的安装与使用(下)
讲师:尚硅谷-宋红康(江湖人称:康师傅)
8. 快捷键的使用
8.1 常用快捷键
见《尚硅谷_宋红康_IntelliJ IDEA 常用快捷键一览表.md》
8.2 查看快捷键
1、已知快捷键操作名,未知快捷键
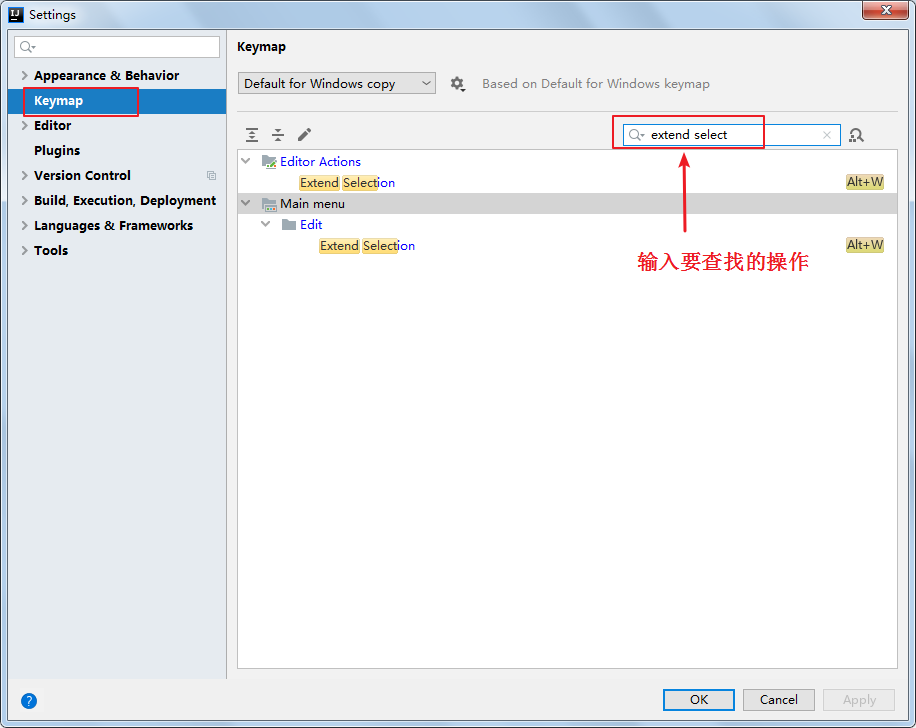
2、已知快捷键,不知道对应的操作名
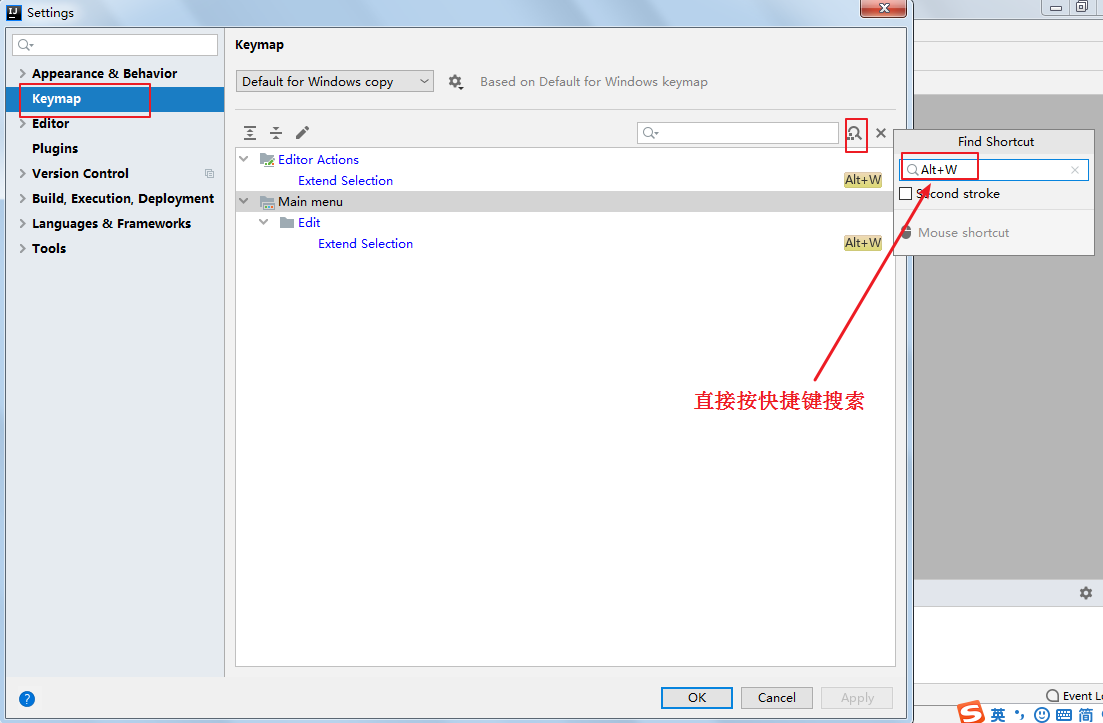
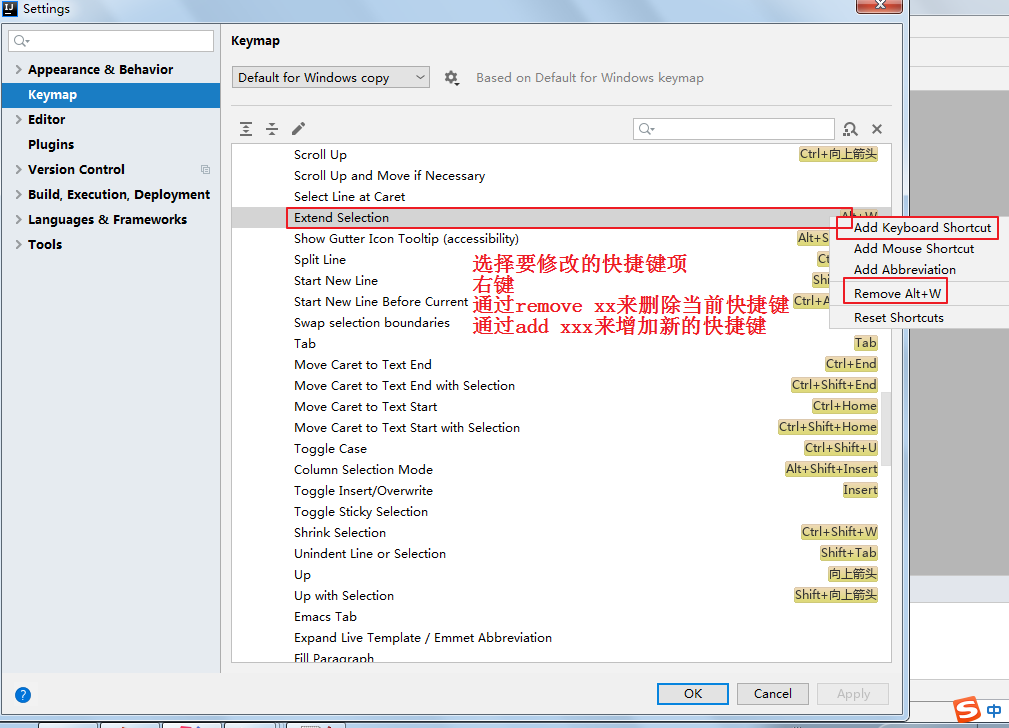
8.3 自定义快捷键
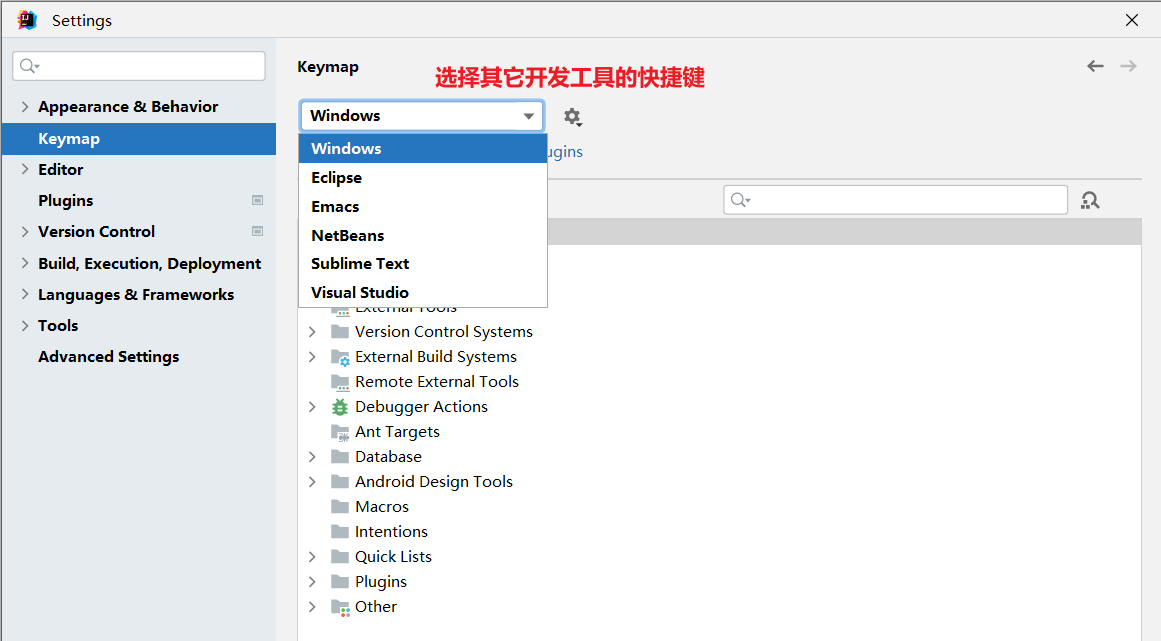
8.4 使用其它平台快捷键
苹果电脑或者是用惯Eclipse快捷的,可以选择其他快捷键插件。
9. IDEA断点调试(Debug)
9.1 为什么需要Debug
编好的程序在执行过程中如果出现错误,该如何查找或定位错误呢?简单的代码直接就可以看出来,但如果代码比较复杂,就需要借助程序调试工具(Debug)来查找错误了。
运行编写好的程序时,可能出现的几种情况:
> 情况1:没有任何bug,程序执行正确!
====================如果出现如下的三种情况,都又必要使用debug=============================
> 情况2:运行以后,出现了错误或异常信息。但是通过日志文件或控制台,显示了异常信息的位置。
> 情况3:运行以后,得到了结果,但是结果不是我们想要的。
> 情况4:运行以后,得到了结果,结果大概率是我们想要的。但是多次运行的话,可能会出现不是我们想要的情况。
比如:多线程情况下,处理线程安全问题。
9.2 Debug的步骤
Debug(调试)程序步骤如下:
1、添加断点
2、启动调试
3、单步执行
4、观察变量和执行流程,找到并解决问题
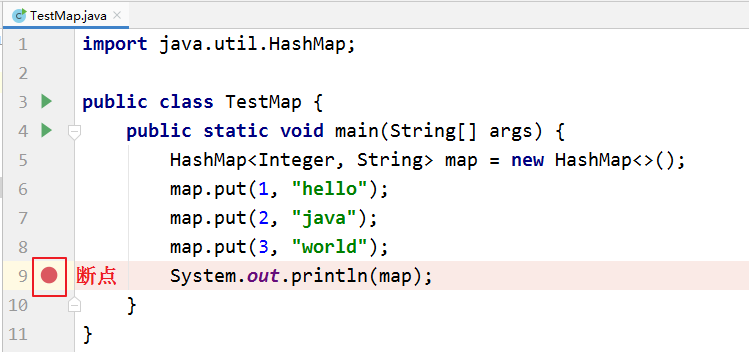
1、添加断点
在源代码文件中,在想要设置断点的代码行的前面的标记行处,单击鼠标左键就可以设置断点,在相同位置再次单击即可取消断点。
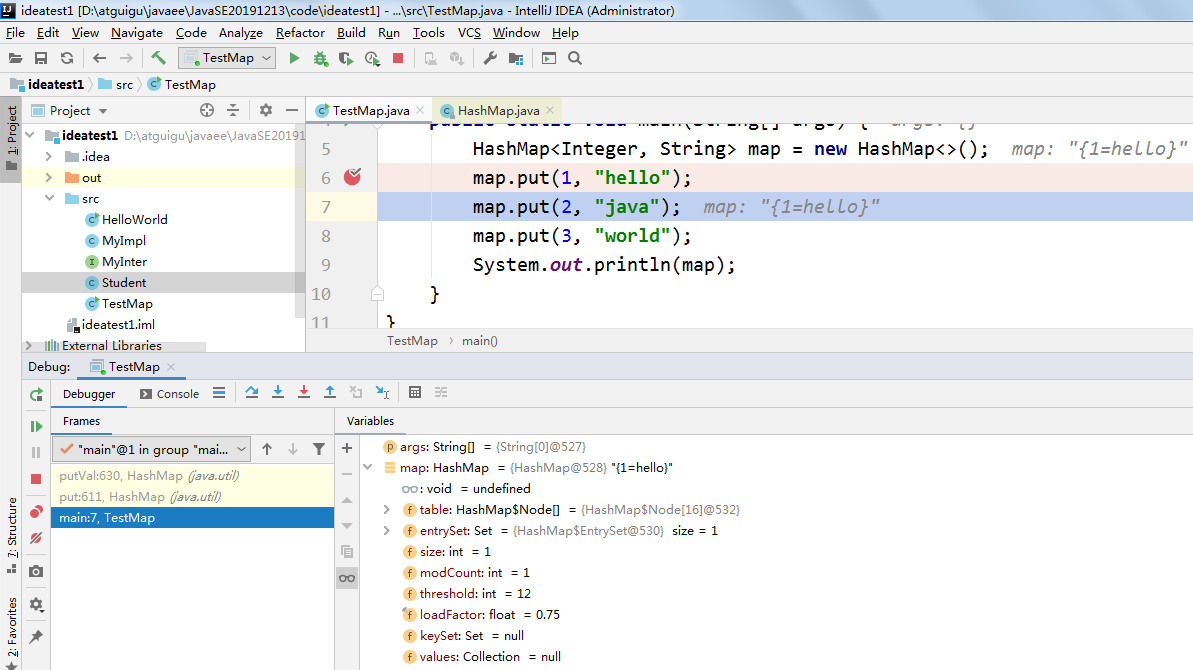
2、启动调试
IDEA提供多种方式来启动程序(Launch)的调试,分别是通过菜单(Run –> Debug)、图标(“绿色臭虫” 等等
等等
3、单步调试工具介绍
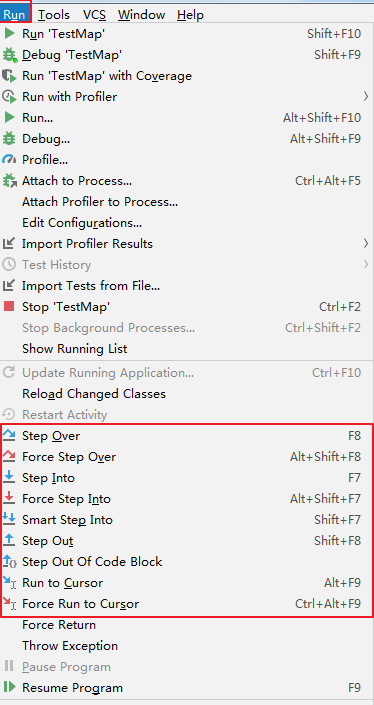
或
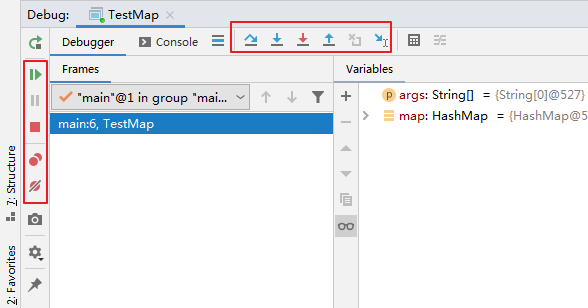
 :Step Over(F8):进入下一步,如果当前行断点是调用一个方法,则不进入当前方法体内
:Step Over(F8):进入下一步,如果当前行断点是调用一个方法,则不进入当前方法体内
 :Step Into(F7):进入下一步,如果当前行断点是调用一个自定义方法,则进入该方法体内
:Step Into(F7):进入下一步,如果当前行断点是调用一个自定义方法,则进入该方法体内
 :Force Step Into(Alt +Shift + F7):进入下一步,如果当前行断点是调用一个核心类库方法,则进入该方法体内
:Force Step Into(Alt +Shift + F7):进入下一步,如果当前行断点是调用一个核心类库方法,则进入该方法体内
 :Step Out(Shift + F8):跳出当前方法体
:Step Out(Shift + F8):跳出当前方法体
 :Run to Cursor(Alt + F9):直接跳到光标处继续调试
:Run to Cursor(Alt + F9):直接跳到光标处继续调试
 :Resume Program(F9):恢复程序运行,但如果该断点下面代码还有断点则停在下一个断点上
:Resume Program(F9):恢复程序运行,但如果该断点下面代码还有断点则停在下一个断点上
 :Stop(Ctrl + F2):结束调试
:Stop(Ctrl + F2):结束调试
 :View Breakpoints(Ctrl + Shift + F8):查看所有断点
:View Breakpoints(Ctrl + Shift + F8):查看所有断点
 :Mute Breakpoints:使得当前代码后面所有的断点失效, 一下执行到底
:Mute Breakpoints:使得当前代码后面所有的断点失效, 一下执行到底
说明:在Debug过程中,可以动态的下断点。
9.3 多种Debug情况介绍
9.3.1 行断点
- 断点打在代码所在的行上。执行到此行时,会停下来。
package com.atguigu.debug;
/**
* ClassName: Debug01
* Package: com.atguigu.debug
* Description: 演示1:行断点 & 测试debug各个常见操作按钮
*
* @Author: 尚硅谷-宋红康
* @Create: 2022/10/20 18:44
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class Debug01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.
int m = 10;
int n = 20;
System.out.println("m = " + m + ",n = " + n);
swap(m, n);
System.out.println("m = " + m + ",n = " + n);
//2.
int[] arr = new int[] {1,2,3,4,5};
System.out.println(arr);//地址值
char[] arr1 = new char[] {'a','b','c'};
System.out.println(arr1);//abc
}
public static void swap(int m,int n){
int temp = m;
m = n;
n = temp;
}
}
9.3.2 方法断点
- 断点设置在方法的签名上,默认当进入时,断点可以被唤醒。
- 也可以设置在方法退出时,断点也被唤醒
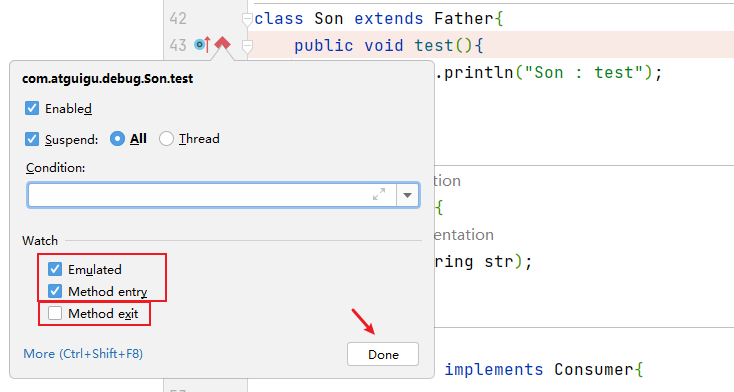
- 在多态的场景下,在父类或接口的方法上打断点,会自动调入到子类或实现类的方法
package com.atguigu.debug;
import java.util.HashMap;
/**
* ClassName: Debug02
* Package: com.atguigu.debug
* Description: 演示2: 方法断点
*
* @Author: 尚硅谷-宋红康
* @Create: 2022/10/20 21:15
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class Debug02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.
Son instance = new Son();
instance.test();
//2.
Father instance1 = new Son();
instance1.test();
//3.
Consumer con = new ConsumerImpl();
con.accept("atguigu");
//4.
HashMap map = new HashMap();
map.put("Tom",12);
map.put("Jerry",11);
map.put("Tony",20);
}
}
class Father{
public void test(){
System.out.println("Father : test");
}
}
class Son extends Father{
public void test(){
System.out.println("Son : test");
}
}
interface Consumer{
void accept(String str);
}
class ConsumerImpl implements Consumer{
@Override
public void accept(String str) {
System.out.println("ConsumerImple:" + str);
}
}
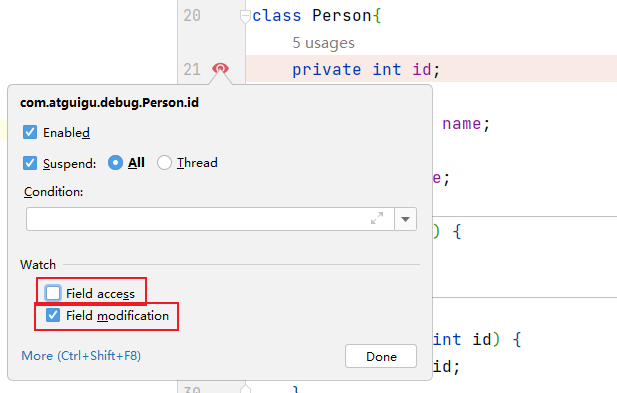
9.3.3 字段断点
- 在类的属性声明上打断点,默认对属性的修改操作进行监控
package com.atguigu.debug;
/**
* ClassName: Debug03
* Package: com.atguigu.debug
* Description: 演示3:字段断点
*
* @Author: 尚硅谷-宋红康
* @Create: 2022/10/20 21:34
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class Debug03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p1 = new Person(3);
System.out.println(p1);
}
}
class Person{
private int id = 1;
private String name;
private int age;
public Person() {
}
{
id = 2;
}
public Person(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public Person(int id, String name, int age) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
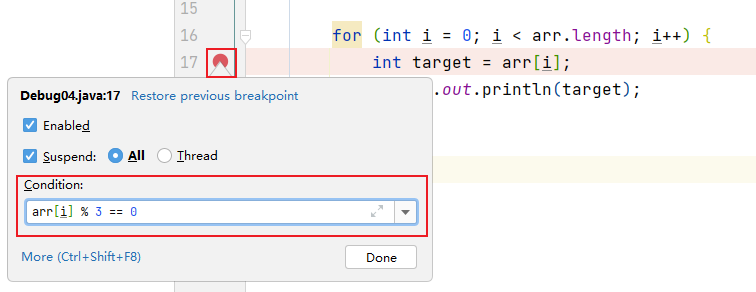
9.3.4 条件断点
package com.atguigu.debug;
/**
* ClassName: Debug04
* Package: com.atguigu.debug
* Description: 演示4:条件断点
*
* @Author: 尚硅谷-宋红康
* @Create: 2022/10/20 21:49
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class Debug04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = new int[]{1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12};
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
int target = arr[i];
System.out.println(target);
}
}
}
针对上述代码,在满足arr[i] % 3 == 0的条件下,执行断点。
9.3.5 异常断点(暂略)
- 对异常进行跟踪。如果程序出现指定异常,程序就会执行断点,自动停住。
package com.atguigu.debug;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* ClassName: Debug05
* Package: com.atguigu.debug
* Description: 演示5:异常断点
*
* @Author: 尚硅谷-宋红康
* @Create: 2022/10/20 22:01
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class Debug05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int m = 10;
int n = 0;
int result = m / n;
System.out.println(result);
// Person p1 = new Person(1001);
// System.out.println(p1.getName().toUpperCase());
}
}
通过下图的方式,对指定的异常进行监控:

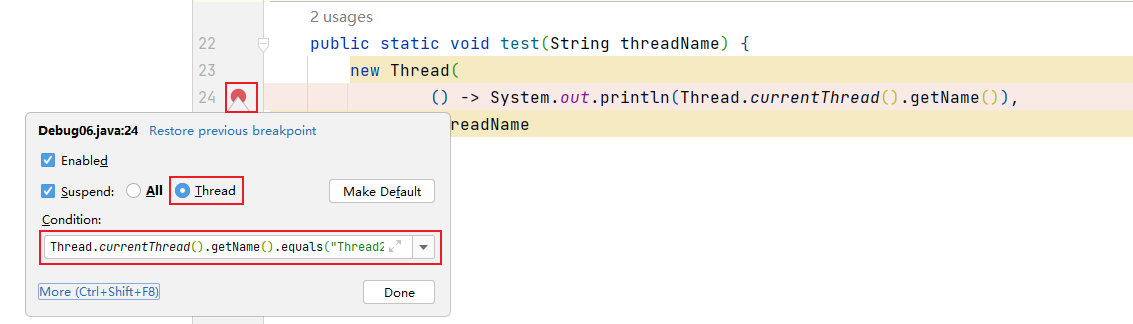
9.3.6 线程调试(暂略)
package com.atguigu.debug;
/**
* ClassName: Debug06
* Package: com.atguigu.debug
* Description: 演示6:线程调试
*
* @Author: 尚硅谷-宋红康
* @Create: 2022/10/20 22:46
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class Debug06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
test("Thread1");
test("Thread2");
}
public static void test(String threadName) {
new Thread(
() -> System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()),
threadName
).start();
}
}
9.3.7 强制结束
package com.atguigu.debug;
/**
* ClassName: Debug07
* Package: com.atguigu.debug
* Description: 演示7:强制结束
*
* @Author: 尚硅谷-宋红康
* @Create: 2022/10/20 23:15
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class Debug07 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("获取请求的数据");
System.out.println("调用写入数据库的方法");
insert();
System.out.println("程序结束");
}
private static void insert() {
System.out.println("进入insert()方法");
System.out.println("获取数据库连接");
System.out.println("将数据写入数据表中");
System.out.println("写出操作完成");
System.out.println("断开连接");
}
}
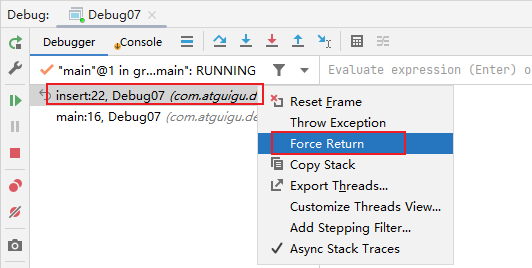
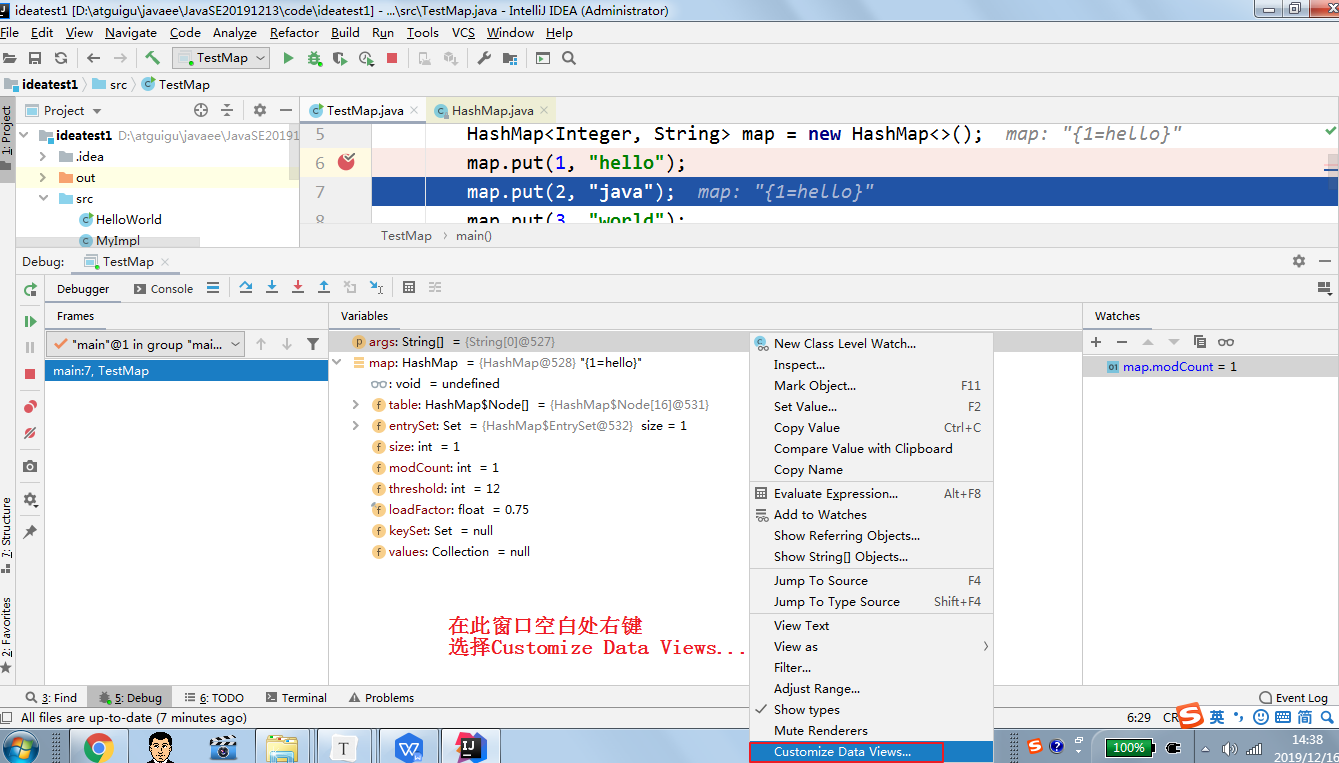
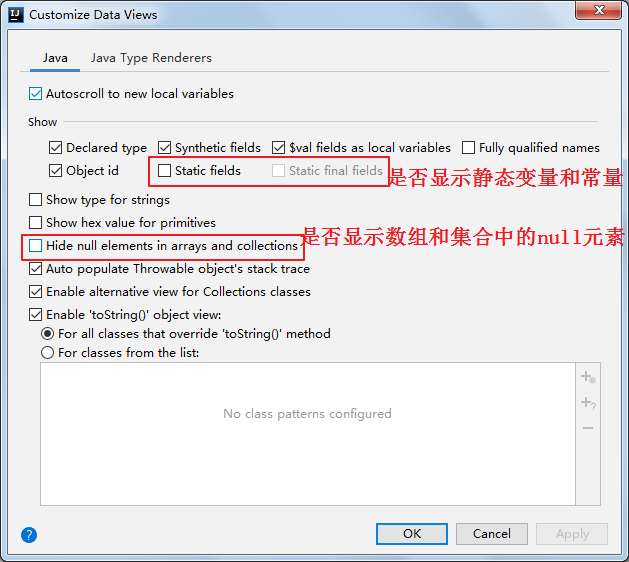
9.4 自定义调试数据视图(暂略)
package com.atguigu.debug;
import java.util.HashMap;
/**
* ClassName: Debug08
* Package: com.atguigu.debug
* Description: 演示8:用户自定义数据视图
*
* @Author: 尚硅谷-宋红康
* @Create: 2022/10/20 23:21
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class Debug08 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<Integer,String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(1,"高铁");
map.put(2,"网购");
map.put(3,"支付宝");
map.put(4,"共享单车");
System.out.println(map);
}
}
设置如下:
9.5 常见问题
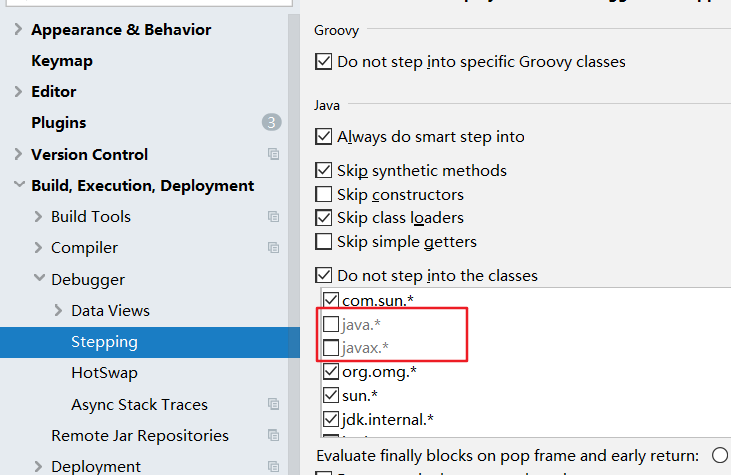
问题:使用Step Into时,会出现无法进入源码的情况。如何解决?
方案1:使用 force step into 即可
方案2:点击Setting -> Build,Execution,Deployment -> Debugger -> Stepping
把Do not step into the classess中的java.*、javax.* 取消勾选即可。
小结:
经验:初学者对于在哪里加断点,缺乏经验,这也是调试程序最麻烦的地方,需要一定的经验。
简单来说,在可能发生错误的代码的前面加断点。如果不会判断,就在程序执行的起点处加断点。
10. IDEA常用插件
推荐1:Alibaba Java Coding Guidelines

阿里巴巴Java编码规范检查插件,检测代码是否存在问题,以及是否符合规范。
使用:在类中,右键,选择编码规约扫描,在下方显示扫描规约和提示。根据提示规范代码,提高代码质量。
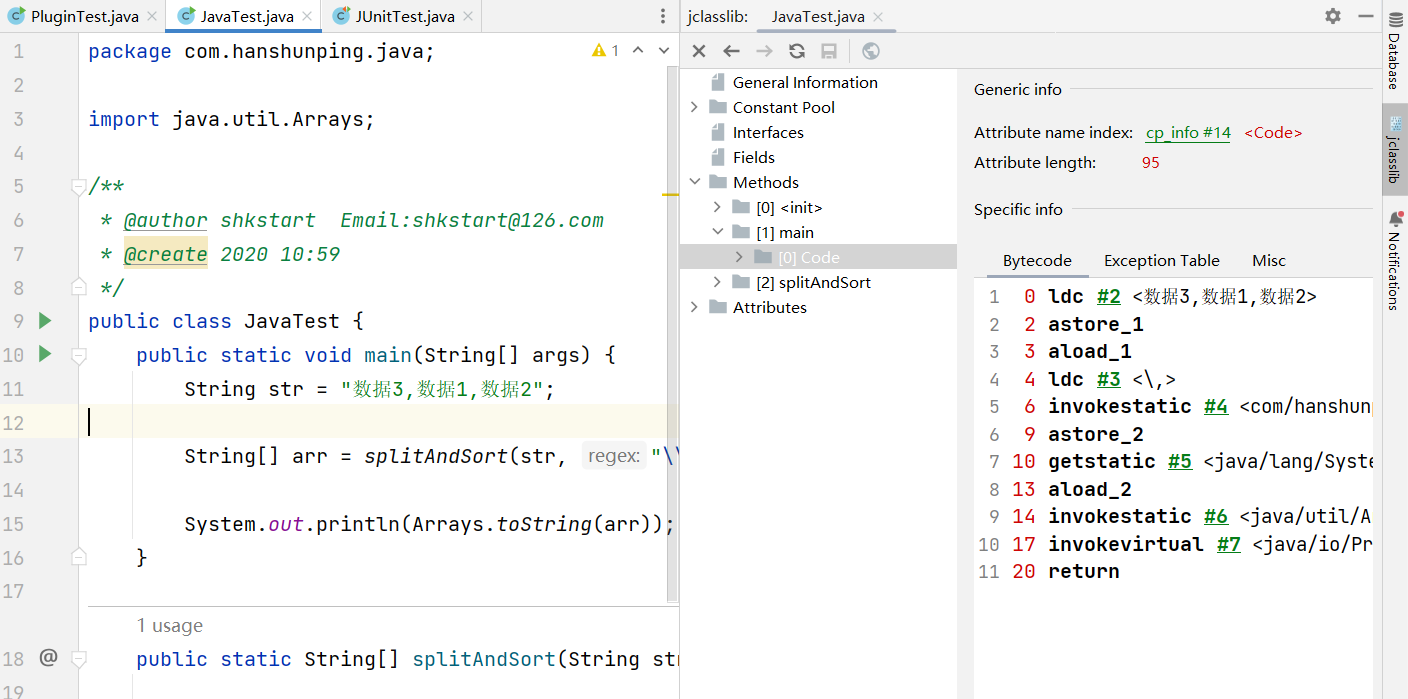
推荐2:jclasslib bytecode viewer

可视化的字节码查看器。
使用:
- 在 IDEA 打开想研究的类。
- 编译该类或者直接编译整个项目( 如果想研究的类在 jar 包中,此步可略过)。
- 打开“view” 菜单,选择“Show Bytecode With jclasslib” 选项。
- 选择上述菜单项后 IDEA 中会弹出 jclasslib 工具窗口。
英文设置:
在 Help -> Edit Custom VM Options …,加上
-Duser.language=en
推荐3:Translation

注册翻译服务(有道智云、百度翻译开放平台、阿里云机器翻译)帐号,开通翻译服务并获取其应用ID和密钥
绑定应用ID和密钥:偏好设置(设置) > 工具 > 翻译 > 常规 > 翻译引擎 > 配置…
使用:鼠标选中文本,点击右键即可自动翻译成多国语言。
注:请注意保管好你的应用密钥,防止其泄露。
推荐4:GenerateAllSetter
实际开发中还有一个非常常见的场景: 我们创建一个对象后,想依次调用 Setter 函数对属性赋值,如果属性较多很容易遗漏或者重复。
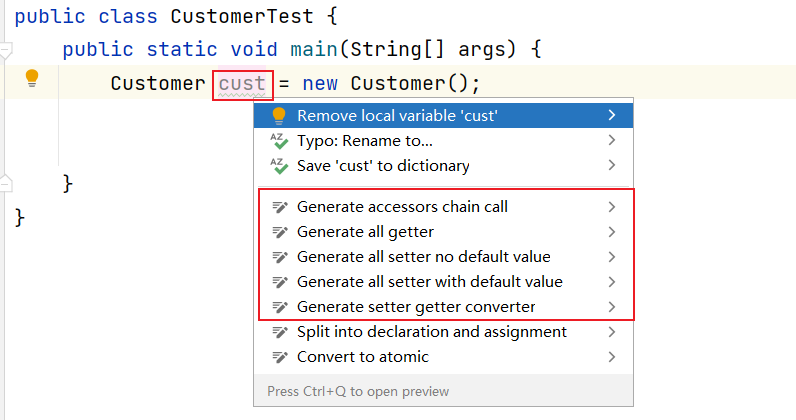
可以使用这 GenerateAllSetter 提供的功能,快速生成对象的所有 Setter 函数(可填充默认值),然后自己再跟进实际需求设置属性值。
插件5:Rainbow Brackets

给括号添加彩虹色,使开发者通过颜色区分括号嵌套层级,便于阅读

推荐6:CodeGlance Pro

在编辑器右侧生成代码小地图,可以拖拽小地图光标快速定位代码,阅读行数很多的代码文件时非常实用。
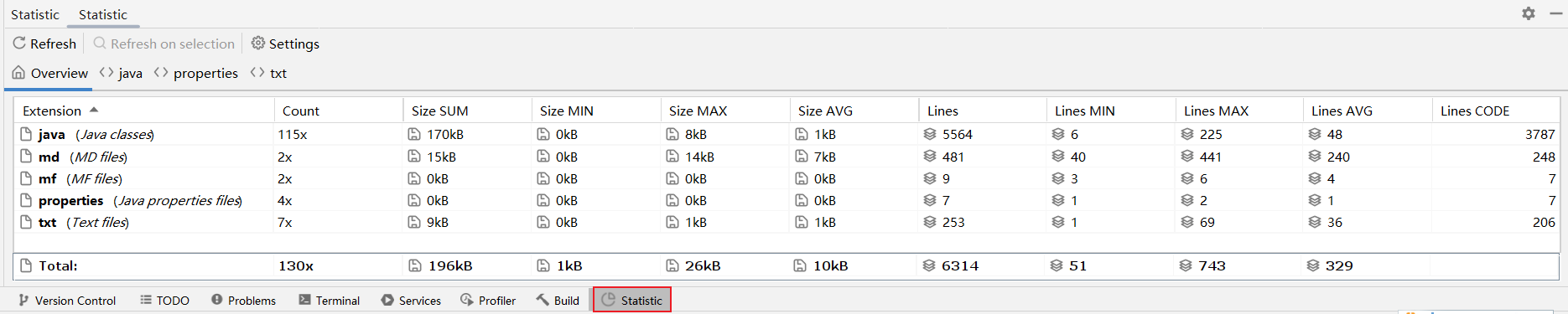
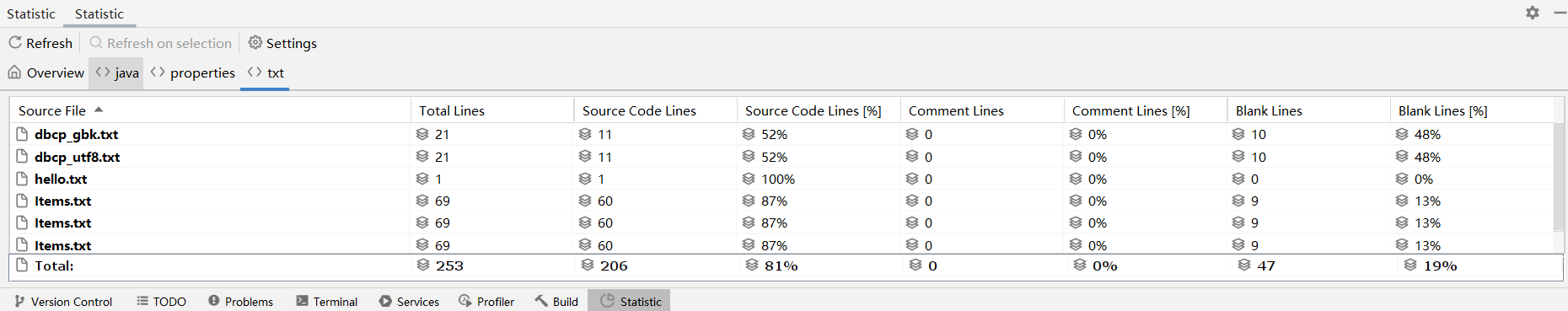
推荐7:Statistic

代码统计工具。
推荐8:Presentation Assistant
显示快捷键操作的按键
推荐9:Key Promoter X
快捷键提示插件。当你执行鼠标操作时,如果该操作可被快捷键代替,会给出提示,帮助你自然形成使用快捷键的习惯,告别死记硬背。
推荐10:JavaDoc
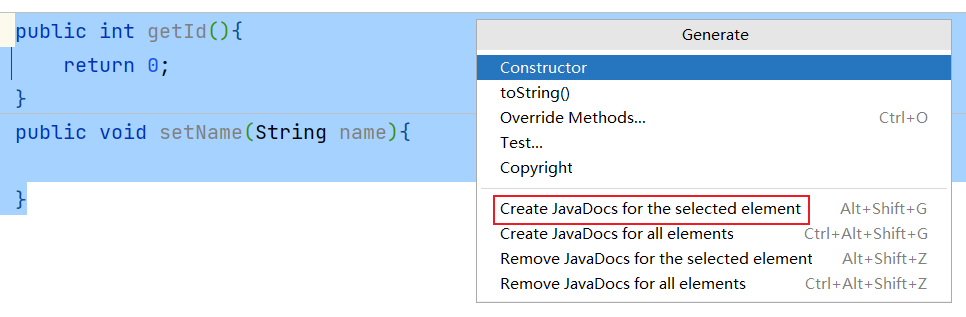
按alt+insert,执行操作:
推荐11: LeetCode Editor

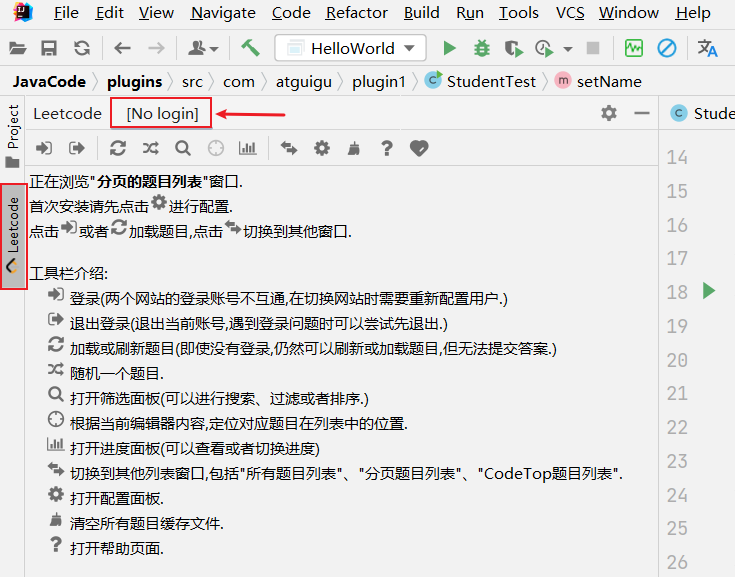
在 IDEA 里刷力扣算法题
推荐12:GsonFormatPlus
根据 json 生成对象。
使用:使用alt + s 或 alt + insert调取。
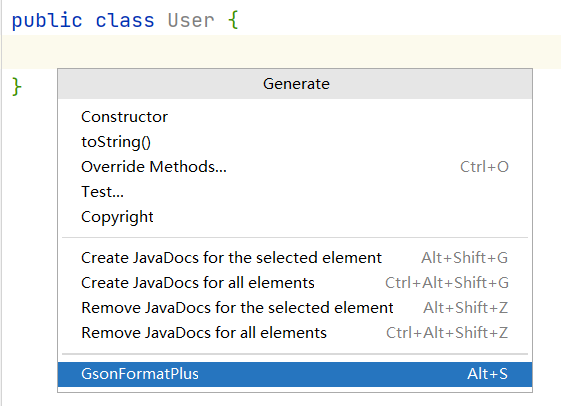
举例:
{
"name": "tom",
"age": "18",
"gender": "man",
"hometown": {
"province": "河北省",
"city": "石家庄市",
"county": "正定县"
}
}
插件13:Material Theme UI

对于很多人而言,写代码时略显枯燥的,如果能够安装自己喜欢的主题将为开发工作带来些许乐趣。
IDEA 支持各种主题插件,其中最出名的当属 Material Theme UI。
安装后,可以从该插件内置的各种风格个选择自己最喜欢的一种。



评论